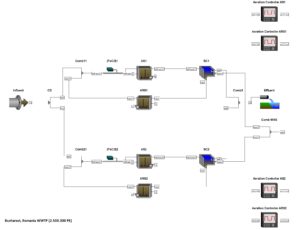
WWTP Modeling has risen as a necessity of the process engineers to assess various operation conditions of a water resource recovery facility (WRRF) that is either existing or simply new designed. Modeling is performed using powerful simulators run on work stations which allows the designing team to model and analyze unlimited time consuming complex operation scenarios of which effect can't be estimated during the design phase.
Modeling of WWTP can be used for sensitivity analysis, to developing flow and mass balance models, and to investigating various interactions among process units or their response individually or as a whole at different hydraulic and pollutant loading.
PARCIS's process engineers provide modeling/simulation services for a variety of treatment layouts, encompassing preliminary, primary, biological and chemical treatment, as well as sludge treatment. The biological treatment modeling provided by the process engineering team is consistent with well accepted activated sludge models (ASM1, ASM2, ASM2d, ASM3, ADM1), developed by the International Water Association task group, but also with new improved alternative approaches as proposed by other peer process engineers groups.
Who could benefit of a WWTP modeling, simulation, optimization ? Here are some examples:
• WWTP Designers and Consultants
• WWTP Contractors
• Water/Wastewater Companies
• WWTP Operators
• Courts of Arbitrations
• Environmental Protection Agency
• National Administration for Surface Waters Management
Without being limited to, the treatment process unite we cane modelled include:
> Preliminary treatment
• Pumping Station
• Equalization Tanks
• Grit Chamber
> Preliminary treatment
• Circular/Rectangular Primary Clarifier
• High Rate Treatment
• In-line Chemical Dosage
> Biological treatment / Suspended Growth Process
• Complete-Mixed Tank
• Anoxic CSTR
• Plug-Flow Tank
• Dual-Inlet Plug-Fow Tank
• Plug-Fow Tank with Aeration Header
• Open Basin HPO
• Membrane Bioreactor (MBR)
• Completely Mixed MBR
• Anaerobic MBR
• Continuous Flow Sequencing Reactor
• Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR)
• Advanced SBR
• Oxidation Ditch
> Biological treatment / Attached Growth Process
• Trickling Filter
• Simple Biological Aerated Filter
• Advanced Biological Aerated Filter
• Rotating Biological Contactor (RBC)
• Submerged Biological Contactor
• Hybrid (Fixed film/Suspended) Reactor
• Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB)
• Membrane-Aerated Bioreactor/Hollow Fibre
> Biological treatment / Secondary Clarifiers
• Circular/Rectangular Primary Clarifier
> Tertiary Treatment
• Upflow Denitrification Filter
• Downflow Denitrification Filter
• Sanf Filter
• Membrane Filter
• Disinfection
• Disc Microscreen
• Advanced Oxidation Process
> Sludge Treatment
• Dissolved Air Flotation
• Gravity Thickener
• Anaerobic Digestion
• Dewatering
• Drum Microscreen
• Hydrocyclone Solids Separation
• Struvite Removal
The most popular biological treatment processes are mainly used for nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus) removal simultaneously with organic matter removal and they include:
> Biological Nitrogen Removal
• BOD/COD removal with nitrification
• BOD/COD removal with nitrification (Modified Ludzak-Ettinger)
• 4-stage Bardenpho
• Step-Feed Denitrifcation
• Simultaneous Denitriifcation
• Alternating Denitriifcation
• Inttermitent Denitriifcation
• Post Denitriifcation
> Biological Phosphorus Removal
• 3-stage Modified Bardenpho (A2O)
• 5-stage Modified Bardenpho
• Johannesburg
• University of Cape Town (UCT)
• Modified University of Cape Town (MUCT)
• Phorodex (A/O)